Hurricanes
It’s hard to go anywhere in North Carolina without being reminded of the impact of hurricanes on our state, past, present, and future. From the name of our professional hockey team to the high-water marks left in riverside communities to the evacuation routes that stand ready to move people out of harm’s way whenever the next storm strikes, our state’s cultural, physical, and psychological landscape has been shaped by these menacing storms.

The warm water in the tropical Atlantic Ocean during the summer and fall is fertile ground, so to speak, for storm formation. Whether these storms track up our coastline or move in as remnant systems from the south, they can make for active seasons all across our state. (For more, see our Tropical Storm Science page.)
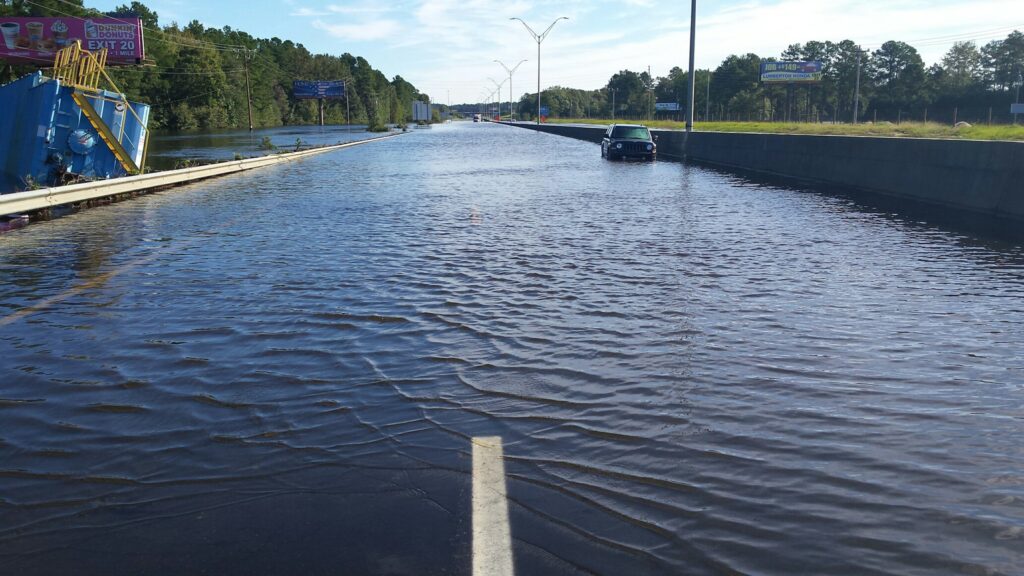
Once they reach us, hurricanes and their remnants can unleash a wide array of impacts, including a storm surge that can overtake coastal communities, heavy rain that causes rivers and streams to swell and flood surrounding areas, gusty winds that can topple rain-weakened trees and power lines, and even severe weather such as tornadoes in their outer bands. (For more, see our Hurricane Hazards page.)
The most impactful hurricanes have literally become household names in North Carolina, from the unrivalled intensity of Hazel to a new generation of Piedmont punishers in Hugo and Fran to the latest set of storms that caused record flooding all across the state, from Floyd to Matthew to Florence to Helene. (For more, see our Notable Storms page.)
The nature of these storms and their impacts is evolving due to global climate change, which is making the ocean surface warmer and thus fueling stronger, faster-intensifying storms. A more moist atmosphere is also helping these storms produce record-breaking rainfall amounts when they reach us. (For more, see our Climate Change and Hurricanes page.)
More Information
Tropical Storm Science
Learn more about how hurricanes form and why they tend to target North Carolina
Hurricane Hazards
Discover the full range of impacts that hurricanes can unleash, and how to prepare
Notable Tropical Storms
Get a history lesson about tropical storms in our state, from the 19th century through the modern era
Climate Change and Hurricanes
Find out how climate change is affecting tropical storms and their impacts on us
Data and Products
Hurricanes Database
View tracks and advisories for all Atlantic tropical systems dating back to 1851

Hurricane Landfalls
Explore historical storms that have made landfall at hurricane strength in North Carolina
Current Conditions
For tropical storm advisories and forecasts, see the National Hurricane Center.